CARBIDE DIE TOOLING
The Lifeblood of a Tool
Carbide die tooling and the production of carbide inserts is the lifeblood of a tool — essentially, it’s the component that makes the tool work. As such, manufacturers need carbide die inserts and tooling processes that produce a reliable product that can withstand the harsh conditions common in today’s manufacturing landscape. However, with so many carbide tooling options in the market, the challenge manufacturers face is identifying the right carbide insert for their application.
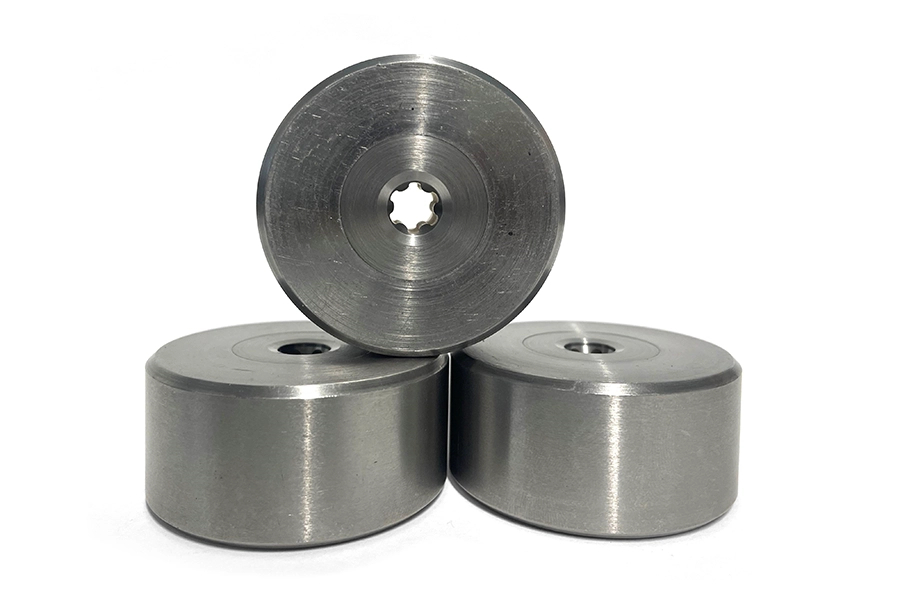

Identifying the Right Carbide Die For Your Industrial Application
One of the more common carbide dies used in tool fabrication is tungsten carbide. Tungsten carbide comes in many different grades that can be categorized based on how much cobalt is added as a binding agent to the actual carbide die. As the percentage of cobalt increases — usually in increments of 6%, 10%, 12%, 15%, 20%, and 25% — the hardness of the carbide die decreases while conversely being able to withstand a harder, more direct hit.
When selecting the right carbide die for your application, another method is to determine the ideal coating to increase carbide wear resistance and lubricity. The right carbide die coating is important as it helps improve essential functions such as wear-resistance and longer durations of elevated working speeds and feeding.
For example, certain additives can be mixed with difficult-to-form metals such as stainless steel to create quality hardness and impact resistance while still allowing the consistent flow of the metal through the tooling process.
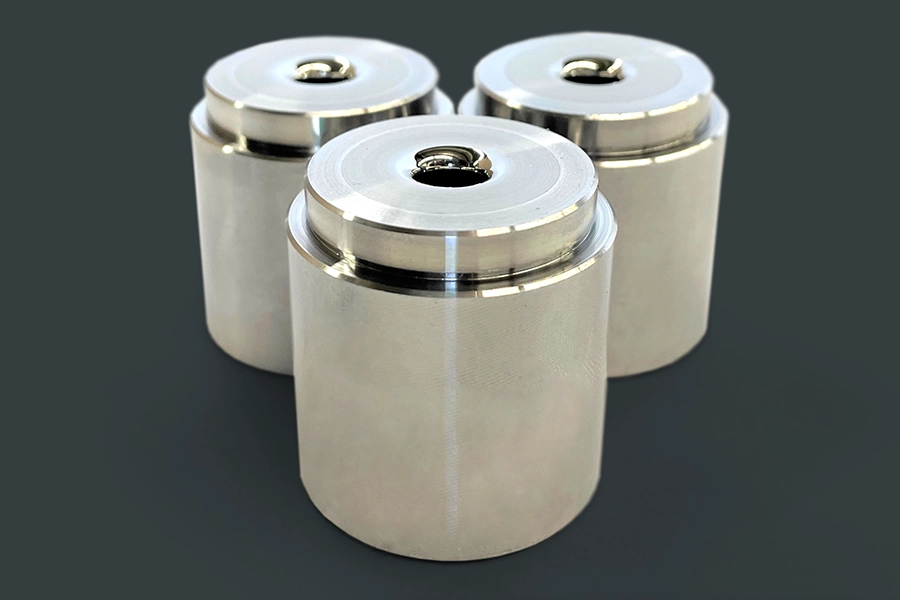

Why Partner with Header for Your Carbide Die Needs?
Our carbide tooling team has years of combined industry experience and knowledge to produce the right carbide product for your application with rapid turnaround times and unmatched quality. Our 40,000 square-foot facility houses state-of-the-art machine and computer technology to help our skilled technicians create custom carbide die solutions for durable tools you need to grow your business.
Our production facility also stocks a wide range of carbide die grades and sizes for fast delivery.
Our robust inventory can meet nearly any size requirement ranging from .200” to 4.75”, and our full line of 25% and 20% Cobalt — along with limited sizes of 15% and 12% Cobalt for harder material needs — means we can start your job as soon as you submit your order. Plus, we offer a wide range of coatings for almost any industrial application.
The coatings listed below can be applied individually or in combination by a physical deposition process (PVD) or a chemical deposition process (CVD).
Our available coating options are:
Titanium Nitride
(TiN)
Titanium Carbonitride
(TiCN)
Titanium Carbide
(TiC)
Titanium Aluminum Nitride
(TiAIN)
Aluminum Titanium Nitride
(AITiN)
Partnering with Header on your carbide die tooling needs will help you experience the productivity and profitability that comes from using tools that were built to last.
CONTACT HEADER DIE & TOOL
See what we can do for you today!
